Wh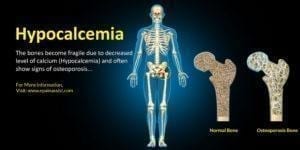 at is Hypocalcemia (Calcium Deficiency) and how to combat it?
at is Hypocalcemia (Calcium Deficiency) and how to combat it?
As most of us are aware, calcium is one of the vital minerals. Our body utilizes this particular mineral for building bones and teeth. Not only this, but calcium is also required for the proper functioning of our heart and other muscles. When your body doesn’t receive sufficient amount of calcium, you will be put at risk of contracting several disorders. In order to put it more clearly, calcium deficiency or what you call it as “Hypocalcemia” is a possibly life-threatening abnormality that carries risks of developing serious disorders like osteoporosis, osteopenia, cardiovascular diseases, high blood pressure, and cancers.
In the following article, let’s see what is hypocalcemia (calcium deficiency) and how to combat it effectively here…
What is the Significance of Calcium?
To start with, if there is something in our body that almost all the tissues and organs use, it is calcium. It is the most abundant mineral present in the body, which performs many vital functions at a time. As mentioned above, it plays a significant role in building bones. Apart from this, calcium is also broadly distributed over the soft tissues, where it will play one of the following roles:
- Neuromuscular function
- Enzymatic function
- Hormonal activities
- Other metabolic activities
So, if you are a person, who averts at the thought of dairy products, you need to strongly reconsider it!
Meeting the Daily Calcium Needs:
Daily consumption, as well as proper absorption of this mineral, is required for supporting an individual’s health. In general, the level of absorption will depend upon the calcium requirements of a person, the food taken, and the quantity of calcium in the food we eat.
Now, let’s see the recommended dietary intake of calcium for different ages:
- 0 to 6 months: 200mg
- 7 to 12 months: 260mg
- 1 to 3 years: 700mg
- 4 to 8 years: 1,000mg
- 9 to 18 years: 1,300mg
- 19 to 50 years: 1,000mg
- 51 to 70 years: 1,000mg for men and 1,200mg for women
- Above 70 years: 1,200mg
One can get a sufficient amount of calcium in the foods taken. Plenty of calcium can be gotten by eating foods rich in calcium. Examples include:
- Milk
- Other dairy products
- Leafy vegetables
- Seafood
- Nuts
- Dried beans
- Orange juice
- Breakfast cereals
- Bread
- Other calcium-fortified products
So, What is Hypocalcemia?
Hypocalcemia or calcium deficiency is a condition that results from insufficient amounts of calcium in our body. Most often, it occurs due to the inadequate consumption of calcium-rich foods for an extended period. Besides this, vitamin D deficiency and inadequate amounts of phosphorus and magnesium can also cause calcium deficiency. It’s because these minerals would help with calcium absorption. Generally, there are two types of calcium deficiency:
Dietary Calcium Deficiency:
As the name suggests, this is caused due to the insufficient intake of calcium, often leading to the depletion calcium reserves in the bones. Thus, it will result in the thinning and weakening of bones, thereby, causing osteoporosis.
Hypocalcemia:
This is the condition that is characterized by a low level of calcium in the bloodstream. Most often, this results as a side effect of the medications like diuretics. Thus, this is not due to the inadequate amount of calcium in the diet. In case of such deficiencies, your body will take calcium from the bones in order to maintain normal calcium levels. Thus, this type of calcium deficiency can eventually result in thinning of bones and osteoporosis.
Hypocalcemia or Calcium Deficiency – Causes:
As mentioned earlier, the primary cause of dietary calcium deficiency is the failure of consumption of recommended amounts of calcium through foods. The second most common cause is the deficiency of other nutrients like vitamin D, magnesium, and phosphorus that are known to improve the calcium absorption. Apart from these, the other known causes of dietary calcium deficiency are:
- Menopause
- Age
- Malabsorption
On the other hand, the primary causes of hypocalcemia are:
- Hypoparathyroidism
- Certain Cancers
- Pancreatitis
- Sepsis
- Diuretics
- Chemotherapy
- Kidney Failure
What are the Symptoms of Calcium Deficiency?
As such, the condition of calcium deficiency won’t be visible during the initial stages. As the condition progresses further, the following signs can be seen:
- Muscle Cramps
- Dry Skin
- Brittle Nails
- Late Puberty
- PMS Symptoms
- Tooth Decay
- Frequent Fractures
- Bone Breakage
- Insomnia
How to Treat Calcium Deficiency?
It’s important to treat calcium deficiency in order to prevent long-term health problems and to retain stronger bones. The condition can be treated in the following ways:
- Changes in Diet:
The calcium deficiency, at its initial stage, can be treated by increasing your intake of calcium-rich foods. Besides this, you are advised to consume foods that have higher amounts of vitamin D, so as to enhance calcium absorption. Apart from this, the calcium deficiency patients are recommended to take either low-fat or fat-free foods to decrease other risks like heart diseases.
- Calcium Supplements:
For the people those who are unable to take sufficient amount of calcium through diet, they can take calcium supplements to cope up with the levels. As such, these supplements are available in various forms like liquid, tablet, and chewable. One such calcium supplement tablet is Calcila from PharmaSynth Formulations.
The composition of Calcila Tablet is as follows:
- Calcium Carbonate
- Dibasic Calcium Phosphate IP (Dihydrate)
- Vitamin D3 IP
- Vitamin B12 IP
- Magnesium Hydroxide IP
- Zinc Sulfate IP
- Lysine Hydrochloride USP
The supplements like Calcila will contain vitamins, minerals, and amino acid, in addition to calcium. Thus, they are not only giving the required amounts of calcium to the recipient but also helping to enhance the calcium absorption. These minerals are known to be essential for maintaining bone health in postmenopausal women. Also, they are used to prevent calcium deficiency in people of all ages.
Who can take Calcila Tablet?
Calcila tablet can be taken by the people with any of the following indications:
- Mild to moderate hypocalcemia
- Hypomagnesaemia
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Osteoporosis
- Osteomalacia
- Osteopenia
- Pregnant women with calcium deficiency
In addition, it can be also be taken to prevent vitamin D deficiency and postmenopausal osteoporosis. For more information on the dosage and warnings, click here.
- Injections:
If changes in diet and calcium supplement tablets don’t yield expected results, your doctor may regulate your calcium levels by giving calcium injections.
Finally, in addition to maintaining a healthy calcium level, you also need to implement some lifestyle changes to enhance your bone health. Those include proper bodyweight, exercises, and reducing your tobacco/alcohol intake.

