Calcila Tablet
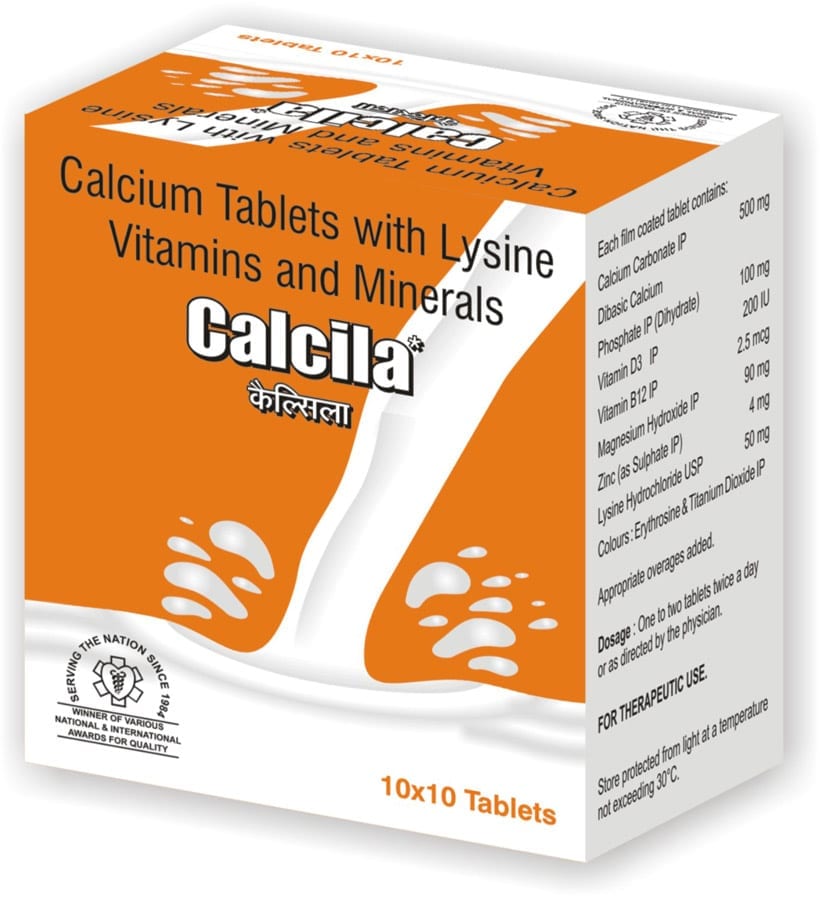
Each film coated tablet contains:» Calcium Carbonate IP 500 mg
» Dibasic Calcium Phosphate IP (Dihydrate)100 mg
» Vitamin D3 IP 200 IU
» Vitamin B12 IP 2.5 mcg
» Magnesium Hydroxide IP 90 mg
» Zinc (as Sulphate IP) 4 mg
» Lysine Hydrochloride USP 50 mg
Description
![]()
![]()
A natural Calcium with lysine and vitamin B12
Composition:
Each film coated tablet contains:
Minerals:
Calcium Carbonate IP 500 mg
Dibasic Calcium Phosphate IP (Dihydrate) 100 mg
Magnesium Hydroxide IP 90 mg
Vitamins:
Vitamin D3 IP 200 IU
Vitamin B12 IP 2.5 mcg
Amino acids:
Lysine Hydrochloride USP 50 mg
Dosage form:
Tablets
ATC classification:
General nutrients
Description:
Calcila tablet is a vitamin-mineral-amino acid dietary supplement containing those vitamins and minerals known to be essential for bone health in postmenopausal women and also to prevent calcium deficiency for all age groups. This formula provides natural Calcium with lysine and vitamin B12. Calcium is necessary for the normal functioning of the nerves, cells, muscles and bone. It is a vital component of bone architecture and is required for deposition of bone mineral throughout life thereby preventing bone loss. It is also associated with a modest reduction in fracture risk. Vitamin D and lysine helps the body to absorb calcium and phosphorus. Having the right amounts of vitamin D, calcium and phosphorus are important for bone health.
Pharmacological action:
Calcium carbonate has the highest percentage of elemental calcium among the calcium salts. Body stores more than 99% of its calcium in the bones and teeth and the rest 1% is found in the extracellular fluid (ECF) or plasma. It is the levels of plasma calcium that dictate calcium balance. If there is plasma calcium deficiency, then the body will take calcium from bones (bone resorption), thereby weakening the bones. Calcium administration decreases the elevated rate of bone resorption and formation over a period of time typically seen in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. It is absorbed in the small intestines with the aid of vitamin D
Dibasic Calcium Phosphate serves as source of calcium and phosphorus. Phosphate plays an important role in the bone resorption and deposition reactions. It interacts with calcium to modify the balance between these two processes. In addition, Phosphorous plays a key role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins and in the formation of ‘high-energy phosphate’ compounds. It also acts as a buffer and plays a role in the renal excretion of sodium and hydrogen ions.
Vitamin D3, also called as cholecalciferol, is produced naturally from 7-dehydrocholesterol when skin is exposed to sunlight. However Vitamin D3 requires metabolic activation. It is transported to the liver where it undergoes hydroxylation to form 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D]. Then 25(OH)D is transported to kidney and released into the renal tubule cell and hydroxylated to form 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D, the biologically active form of vitamin D also known as Calcitriol. Calcitriol stimulates intestinal calcium transport and also release of calcium from bone, thereby maintaining plasma calcium levels. Adequate dietary supplementation of Vitamin D3 is required because in deficient states, inadequate absorption of calcium from intestine leads to increased calcium resorption from the bone. This causes rickets in children while osteoporosis and osteomalacia in adults.
Vitamin B12 is present in the body mainly as methylcobalamine, adenosylcobalamine and hydroxocobalamine. Deficiency of vitamin B12 interferes with haemopoiesis and produces megaloblastic anaemia. Decreased bone mineral density may be associated with low levels of vitamin B12.
Lysine is one of nine essential amino acids required for growth and tissue repair. It aids in the production of antibodies, enzymes and hormones. It aids in the absorption of calcium and formation of collagen thereby promoting bone cartilage health. It is effective against herpes simplex viruses by interfering with the viral growth by balancing the nutrients
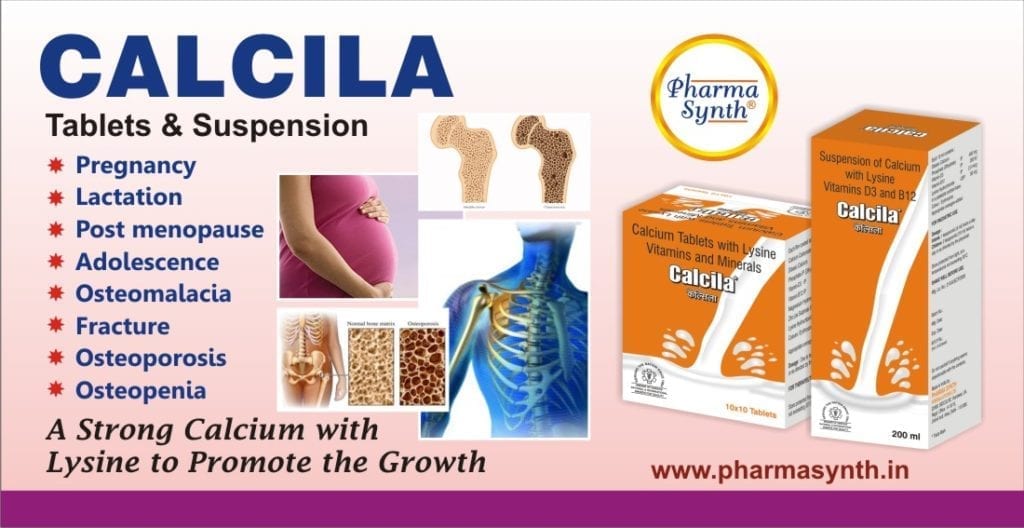
Indications:
- Mild to moderate hypocalcemia characterized by low degree of tetany.
- Hypocalcaemia and hypomagnesaemia after small bowel resection.
- Vitamin D deficiency states
- Prevention of Vitamin D deficiency.
- Osteoporosis
- Prevention of Post-Menopausal Osteoporosis.
- Osteomalacia
- Osteopenia
- In pregnant women it is to be indicated only in deficiency states or as prescribed by physician.
Dosage:
- Calcium is best absorbed in doses of 500 mg or less
- Do not exceed calcium 2500 mg/day in men or 2000 mg/day in women (Hypercalcemia risk)
- Daily dose of 1000 mg Calcium Indications:
- Men and women ages 25 to 50 years
- Men 50 to 65 years
- Women on Estrogen Replacement ages 50-65 yearS
- Daily 1 tablet or as recommended by physician if indicated for vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
Contraindications:
- Hypersensitivity to the any of the ingredients.
- Renal failure.
- Diseases and/or conditions resulting in hypercalcaemia and/or hypercalciuria (e.g. myeloma, bone metastases, primary hyperparathyroidism).
- Nephrolithiasis/nephrocalcinosis.
- Because of phosphate content, it is contraindicated in persons with hypoparathyroidism.
- Hypervitaminosis D.
- Malabsorption syndrome
Side effects:
No side effects have been observed with Calcila tablets when taken at recommended doses.
Uncommon side effects: Hypercalcaemia and hypercalciuria.
Rare: Constipation, flatulence, nausea, abdominal pain, and diarrhea, pruritus, rash and urticaria
Warnings and Precautions:
General:
Serum and urinary calcium levels along with renal function should be monitored in the following:
- During long-term treatment.
- In patients with a high tendency to calculus formation
- In elderly patients on concomitant treatment with cardiac glycosides or diuretics.
It should be prescribed with caution to patients suffering from sarcoidosis, due to the risk of increased metabolism of vitamin D into its active form
It is to be used with caution in immobilized patients with osteoporosis due to the increased risk of hypercalcaemia.
Drug Interactions:
The following drugs are known for having drug interactions with calcium-vitamin D supplements:
Thiazide diuretics
Systemic corticosteroids
Ion exchange resins
Tetracyclines
Cardiac glycosides
Pregnancy:
Calcila tablet can be used deficiency states only however daily intake should not exceed 1,500 mg calcium and 600 IU vitamin D.
Lactation:
Calcium-Vitamin D passes into breast milk. Hence this should be taken into consideration while prescribing additional Vitamin D to the child.
References:
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2621390/
pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5280795#section=Drug-and-Medication-Information
pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5283711#section=Therapeutic-Uses
aminoacidstudies.org/
Disclaimer:
- Information provided above is for reference purpose only and has been compiled for use by healthcare practitioners. Please consult your physician to understand how the product affects you, its dosages, side-effects and further information.
- Remember, keep this and all other medicines out of the reach of children, never share your medicines with others, and use this medication only for the indications prescribed by your physician.
- Every effort has been made to ensure that the information provided by Pharma Synth Formulations Ltd. (‘PSFL’) is accurate, up-to-date, and complete, but no guarantee is made to that effect. PSFL does not endorse drugs, diagnose patients or recommend therapy and is an informational resource designed to assist licensed healthcare practitioners in caring for their patients and/or to serve consumers viewing this service as a supplement to, and not a substitute for, the expertise, skill, knowledge and judgment of healthcare practitioners. PSFL does not assume any responsibility for any aspect of healthcare administered with the aid of information provided. The information contained herein is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, warnings, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or adverse effects. If you have questions about the drugs you are taking, check with your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.