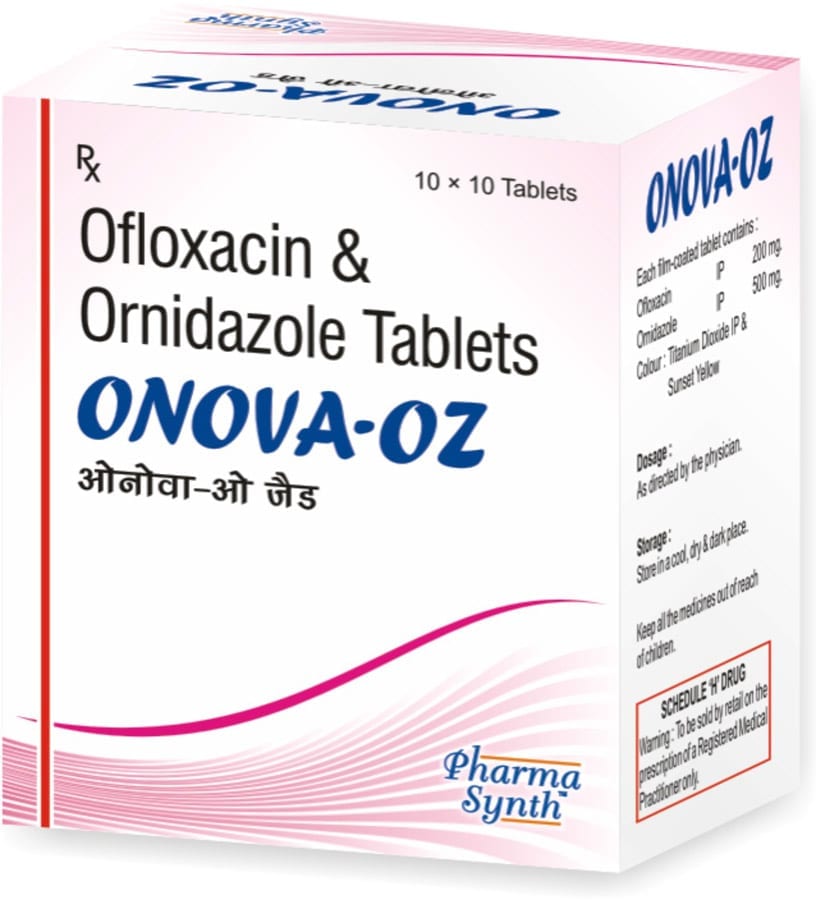
ONOVA-OZ
Each film-coated tablet contains:
» Ofloxacin IP 200 mg
» Ornidazole IP 500 mg
Excipients q.s.
Description
![]()
Excellent ofloxacin with proteolytic advantages.
Composition:
Each film-coated tablet contains:
Ofloxacin IP 200 mg
Ornidazole IP 500 mg
Excipients q.s.
Dosage form:
Tablets
ATC classification:
Broad spectrum antibiotic
Description:
ONOVA-OZ tablet facilitates concomitant administration of an antibacterial and an anti protozoal drug. Ofloxacin is the quinolone antibacterial component of Onova-oz whereas Ornidazole has both antiprotozoal and antibacterial activity. It is designed for treating diarrhea and peritonitis caused in adults due to bacteria, amoeba and/or mixed origin.
Pharmacological action:
Ofloxacin: It is active after oral administration. It exhibits antibacterial activity by inhibiting DNA topo-isomerases mainly DNA gyrase, the enzyme involved in DNA replication of bacteria.
Ofloxacin has antibacterial activity against most strains of the following microorganisms both in vitro and in clinical infections:
Aerobic Gram-positive Microorganisms
Staphylococcus aureus(methicillin-susceptible strains)
Streptococcus pneumoniae(penicillin-susceptible strains)
Streptococcus pyogenes
Aerobic Gram-negative Microorganisms
Citrobacter (diversus) koseri
Enterobacter aerogenes
Escherichia coli
Haemophilus influenzae
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Proteus mirabilis
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Pharmacokinetics of Ofloxacin:
It is completely absorbed after oral administration. Maximal drug concentration in blood reaches within 1-3hrs after dosing and elimination half life is 4-6hrs. It is primarily excreted unchanged in urine.
Following oral administration of recommended therapeutic doses, ofloxacin has been detected in skin, sputum, lung tissue, blister fluid, ovary, cervix, prostatic fluid and prostatic tissue. The mean concentration of ofloxacin in each of these various tissues and body fluids after one or more doses was 0.8 to 1.5 times the concurrent plasma level.
Ornidazole: It passively enters the bacterial cell wall where its nitro group is reduced to amine group by the redox system of bacteria. The intermediate intracellular metabolites thus formed during the redox reactions are believed to be causing bacterial cell death. The same mechanism of action is postulated in protozoa.
Ornidazole is effective against the following protozoa:
Trichomonas vaginalis, Entamoeba histolytica and Giardia lamblia (Giardia intestinalis),
And also against certain anaerobic bacteria such as Bacteroides and Clostridium spp., Fusobacterium spp., and anaerobic cocci.
Pharmacokinetics of Ornidazole:
Following oral administration, ornidazole is rapidly absorbed and peak plasma concentrations of 30mcg/ml are reached within 2 hours of single dose of 1.5gms. Food affects the rate of absorption of Ornidazole. It has less affinity to plasma proteins and readily distributes to body tissues, fluids and cerebrospinal fluid. Antibacterial concentrations are achieved in intestinal tissues, vaginal secretions and amniotic fluids. More than 90% of Ornidazole is metabolized in liver and the metabolites have anti bacterial activity against anaerobic bacteria. Elimination half life is 12-14hours. It is excreted in urine as conjugates and metabolites. However biliary excretion is important in elimination of Ornidazole and its metabolites.
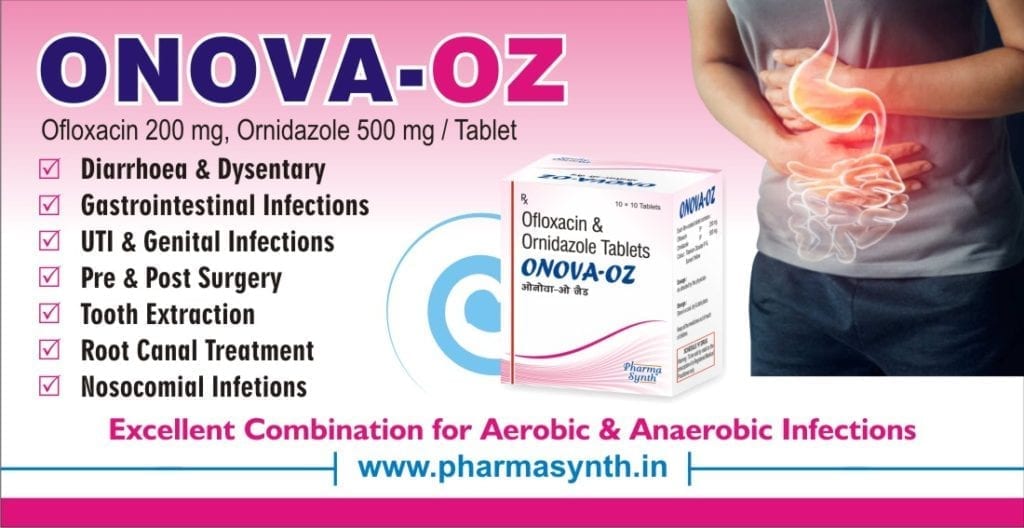
Indications:
ONOVA-OZ is indicated for:
- Diarrhoea and dysentery
- Pelvic Inflammatory disease
- Post surgical care
- Prophylaxis in elective surgery
- Post Appendectomy
- Intra-abdominal infections
- Hernia Repair
- Dental infections
- Root canal infections
- Periapical abscess
- Periodontal abscess
- Pre & post-operative care
- ENT infections
- Skin and soft tissue infections
- Foot ulcers especially in diabetes
- Lung abscess
- Infections in immunocompromised patients
Dosage
One tablet of ONOVA- OZ is recommended as twice-daily therapy.
Contraindications:
ONOVA- OZ is contraindicated in persons with a history of hypersensitivity associated with the use of ofloxacin, ornidazole or any member of the quinolone or nitroimidazole group of antimicrobial agents.
Side effects:
- Headache is the commonly reported side effect
- Other side effects occurring to lesser extent are nausea, vomiting.
- Abdominal cramps are most common
- Occasionally diarrhea and dryness of mouth
- External genital itching in women ,vaginal inflammation (vaginitis)
- Taste changes
Warnings and Precautions:
Ofloxacin:
- Fluoroquinolone antibiotics, including ofloxacin, are associated with an increased risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture in all ages. The risk of developing fluoroquinolone-associated tendinitis and tendon rupture is further increased in older patients, usually over 60 years of age, in those taking corticosteroid drugs, and in patients with kidney, heart or lung transplants.
Note: Tendinitis and tendon rupture have been reported in patients taking fluoroquinolones who do not have the above mentioned risk factors and therefore Ofloxacin should be discontinued if the patient experiences pain, swelling, inflammation or rupture of a tendon. Patients are advised to rest at the first sign of tendinitis or tendon rupture, and to contact their physician regarding changing to a non-quinolone antimicrobial drug
- Ofloxacin is known to exacerbate myasthenia gravis
- The following CNS effects have been reported by patients receiving quinolones, including ofloxacin: convulsions, increased intracranial pressure, (including pseudotumourcerebri), and toxic psychosis. They are known to cause central nervous system (CNS) stimulation,which may lead to tremors, restlessness/agitation, nervousness/anxiety, lightheadedness, confusion, hallucinations, paranoia and depression, nightmares, insomnia and, rarely, suicidal thoughts or acts. These reactions may occur following the first dose.
Note: If these reactions occur in patients receiving ofloxacin, the drug should be discontinued and appropriate measures instituted. Insomnia is common with ofloxacin than some other products in the quinolone class. As with all quinolones, ofloxacin should be used with caution in patients with a known or suspected CNS disorder that may predispose to seizures or lower the seizure threshold (e.g. severe cerebral arteriosclerosis, epilepsy) or in the presence of other risk factors that may predispose to seizures or lower the seizure threshold (e.g. certain drug therapy, renal dysfunction).
- Ofloxacin should be avoided in patients with known prolongation of the QT interval (torsades de pointes), patients with uncorrected hypokalaemia, and patients receiving Class IA (quinidine, procainamide), or Class III (amiodarone, sotalol) anti-arrhythmic agents.
Ornidazole:
- Before prescribing ornidazole caution should be exercised in patients with diseases of the CNS, e.g.epilepsy or multiple sclerosis. The effect of other medicines can be intensified or impaired.
Drug Interactions:
The following drugs are known for having drug interactions with Ofloxacin:
- Antacids, Sucralfate, Metal Cations, and Multivitamins should not be taken within the 2-hour period before or within the 2-hour period after ofloxacin administration.
- Cimetidine, NSAIDs, Anti-diabetic drugs, drugs metabolized by cytochromeP-450 enzymes and warfarin like anti-coagulants.
The following drugs are known for having drug interactions with Ornidazole:
- In contrast to other nitroimidazole derivatives, ornidazole does not inhibit aldehyde dehydrogenase and is, therefore it is not incompatible with alcohol.
- Ornidazole potentiates the effect of coumarin type oral anticoagulants.
- Ornidazole prolongs the muscle-relaxant effect of vecuronium bromide.
Pregnancy:
No adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women to determine safety of ONOVA-OZ
Lactation:
Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from ofloxacin in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
References:
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/ofloxacin#section=Top
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Ornidazole
Disclaimer:
- Information provided above is for reference purpose only and has been compiled for use by healthcare practitioners. Please consult your physician to understand how the product affects you, its dosages, side-effects and further information.
- Remember, keep this and all other medicines out of the reach of children, never share your medicines with others, and use this medication only for the indications prescribed by your physician.
- Every effort has been made to ensure that the information provided by Pharma Synth Formulations Ltd. (‘PSFL’) is accurate, up-to-date, and complete, but no guarantee is made to that effect. PSFL does not endorse drugs, diagnose patients or recommend therapy and is an informational resource designed to assist licensed healthcare practitioners in caring for their patients and/or to serve consumers viewing this service as a supplement to, and not a substitute for, the expertise, skill, knowledge and judgment of healthcare practitioners. PSFL does not assume any responsibility for any aspect of healthcare administered with the aid of information provided. The information contained herein is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, warnings, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or adverse effects. If you have questions about the drugs you are taking, check with your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.