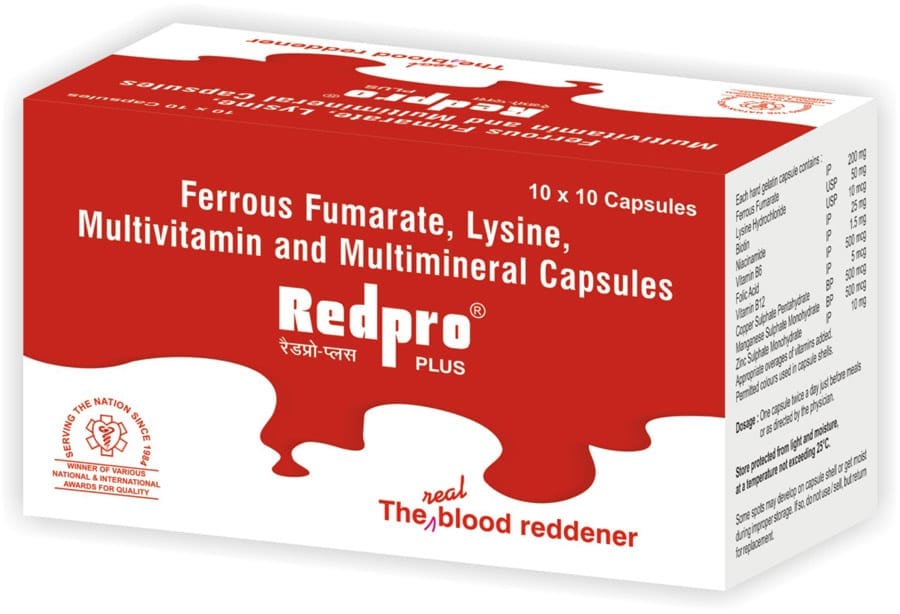
Redpro PLUS Capsules
Each hard gelatin capsule contains :
» Ferrous Fumarate IP 200mg
» Lysine Hydrochloride USP 50 mg
» Biotin USP 10 mcg
» Niacinamide IP 25 mg
» Vitamin B6 IP 1.5 mg
» Folic Acid IP 500 mcg
» Vitamin B12 IP 5 mcg
» Copper Sulphate BP 500 mcg
» Manganese Sulphate BP 500 mcg
» Zinc Sulphate IP 10 mg
Description
![]()
A complete Haematinic with Zinc & Lysine (in Sorbitol base)The Real Blood Reddener.
Redpro PLUS capsules
Composition:
Each hard gelatin capsule contains :
Ferrous Fumarate IP 200mg
Lysine Hydrochloride USP 50 mg
Biotin USP 10 mcg
Niacinamide IP 25 mg
Vitamin B6 IP 1.5 mg
Folic Acid IP 500 mcg
Vitamin B12 IP 5 mcg
Copper Sulphate BP 500 mcg
Manganese Sulphate BP 500 mcg
Zinc Sulphate IP 10 mg
Dosage form:
Capsules
ATC classification:
Haematinics
Description:
Redpro Plus is a haematinic containing all the necessary vitamins, minerals and aminoacids that are essential for the proper formation of the components of blood. The formula is designed to treat the iron deficiency anemia and as prophylaxis in pregnant women, to prevent birth defects and to protect from congenital malformations. Redpro Plus offers iron in ferrous form which gets absorbed thrice as much as that of ferric iron gets absorbed. Iron is necessary for the synthesis of hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying component of the red blood cells. Folic acid and Vitamin B12 are necessary for hemopoiesis, the synthesis and maturation of red blood cells. Vitamin B6 is not only essential for synthesis of hemoglobin but also increases oxygen carrying capacity of hemoglobin. Deficiency in either of Vitamin B6, Folic acid or Vitamin B12 leads to vitamin deficient anemia.
Pharmacological action:
Ferrous fumarate, the fumarate salt form of the mineral iron, when administered elevates serum iron concentration. Then the iron gets assimilated into hemoglobin which is made of four protein subunits, with each subunit having an iron moiety. It is required for the transport of oxygen. Iron also gets trapped in the reticuloendothelial cells for storage. Iron is also an important enzymatic mineral in the synthesis of myoglobin.
Pharmacokinetics of Ferrous fumarate:
Iron is absorbed in duodenum and upper jejunum. In anemic patients, absorption is increased to 20%-30% compared to those of people with adequate iron. Fewer side effects with ferrous fumarate are attributed to its low solubility and slow dissolution rate after oral administration. Also, the rate of release of ferrous ions from ferrous fumarate is slower than that from the highly soluble ferrous sulfate. It is primarily bound to serum transferring in its ferric form. Iron has half life of 6 hours. It is excreted in urine, sweat, sloughing of intestinal mucosa and by menstrual cycle in women.
Lysine hydrochloride has beneficial effects in absorption of iron and in anemia. In pregnant women addition of lysine to iron and vitamin supplements maintains significantly higher mean hemoglobin levels throughout pregnancy and also at 3 days post partum. It has also been reported that lysine in combination with ferrous fumarate and pyridoxine is more effective in treating iron deficiency anemia in pregnant women compared to women only on ferrous fumarate. Moreover lysine is one of nine essential amino acids required for growth and tissue repair. It aids in the production of antibodies, enzymes and hormones. It aids in the absorption of calcium and formation of collagen thereby promoting bone cartilage health. It is effective against herpes simplex viruses by interfering with the viral growth by balancing the nutrients.
Biotin is a water-soluble B-complex vitamin. It functions as a cofactor for carboxylase enzymes involved in liver gluconeogenesis. Four of the 5 biotin-dependent carboxylases are in the mitochondria. They are involved in the synthesis of heme and amino acids. It has been postulated that biotin deficiency causes heme deficiency, decreases heme content and synthesis. It also triggers oxidative damage to the cells.
Niacinamide (Vit-B3) is required for the functioning of the coenzymes nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP). NAD and NADP are necessary for tissue respiration; glycogenolysis; and lipid, amino acid, protein, and purine metabolism. Its deficiency leads to pellagra. It also has putative activity against osteoarthritis and granuloma annulare. It has been postulated that combining Niacinamide with cyanocobalamin and folic acid is effective in treating megaloblastic anemia.
Vitamin B6 once absorbed, converts to the co-enzymes, pyridoxamine phosphate and pyridoxal phosphate, which functions as a coenzyme in the metabolism of amino acids, glycogen and protein.
Folic acid also known as Vitamin B9 is an essential nutrient that is required for DNA replication and for enzymatic reactions involved in amino acid synthesis and vitamin metabolism. Deficiencies of folate due to genetic defects, reduced intake, increased metabolism, and/or increased requirements leads to hyperhomocysteinemia, megaloblastic anemia, and mood disorders. It is also required for growth and development of fetus. Its deficiency in pregnant women has been associated with abnormalities in both mothers (anemia, peripheral neuropathy) and fetuses (congenital abnormalities). It has been found that folic acid supplementation around the time of conception reduces the risk of neural tube defects in the offspring.
Vitamin B12 also known as Cyanocobalamine is present in the body mainly as methylcobalamine, adenosylcobalamine and hydroxocobalamine. Deficiency of vitamin B12 interferes with haemopoiesis and produces megaloblastic anaemia. Vitamin B12 along with folic acid improve fetal brain development and prevent neural tube defects.
Copper is essential for the normal growth and development of human fetuses and infants. Recommended oral intake of copper for pregnant women is 1mg/day and for nursing mothers is 1.3mg/day. Copper availability is hindered due to iron and zinc. Hence, pregnant women taking iron and zinc supplements should have even copper in their supplements. It has been reported that women having preeclampsia during pregnancy are usually deficient in copper.
Manganese sulphate in Redpro Plus provides manganese to the body. Manganese is an essential mineral nutrient in humans that is required for normal amino acid, lipid, protein, and carbohydrate metabolism. Functionally, manganese acts by activating certain enzymes (many hydrolases, kinases, decarboxylases, and transferases) or through manganese-dependent metalloenzymes that are needed for proper immune function, regulation of blood sugars and cellular energy, reproduction, digestion, bone growth, and the body’s defense against free radicals.
Zinc sulphate present in Redpro Plus provides zinc, which is an essential nutrient to the body. Zinc supplementation decreases oxidative stress markers and generation of inflammatory mediators. Zinc has therapeutic efficacy in treating acute infantile diarrhea, common cold and acrodermatitis enteropathica. A low serum zinc level in pregnant women has been implicated in incidence of complications affecting mothers and infants.
Indications:
Redpro Plus capsules are indicated for the following
- Pregnant and lactating women
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Dietary insufficiency
- Chronic or acute blood loss during menstrual cycle
- Post surgical care
- Malabsorption
- Lactating women who gave birth to premature babies
- During the treatment of pernicious anemia
- Worm infestations
- Tuberculosis patients
- General debility
- Menarche to menopause
Dosage:
- Daily one capsule, or as recommended by the physician.
- In pregnant and lactating women dosage should be prescribed based on the stage of pregnancy and iron levels of lactating women respectively.
Contraindications:
RedproPlus is contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to ferrous fumarate, folic acid or to any other component of this formulation.
Redpro Plus is contraindicated in Hemosiderosis, hemochromatosis, hemolytic anemia, porphyria cutanea tarda, peptic ulcer disease, regional enteritis, ulcerative colitis.
Side effects:
Common side effects: Heartburn, nausea, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, dark stools and constipation.
Occasional side effects: extrinsic stain on teeth.
Side effects with iron therapy are usually transient. Gastrointestinal side effects are relatively common and corrective bowel regimens such as increasing dietary fibre or over-the-counter medications might be recommended to balance the side effects due to Iron therapy.
Chronic administration of iron may lead to hemosiderosis.
Warnings and Precautions:
General:
- Do not exceed the recommended dose.
- Large doses of iron may aggravate gastrointestinal diseases such as peptic ulcer disease, regional enteritis and ulcerative colitis.
- The type of anaemia and the underlying cause or causes should be determined before starting therapy with RedproPlus. Since the anaemia may be a result of a systemic disturbance, such as recurrent blood loss, the underlying cause or causes should be determined and corrected.
- It is recommended that for people with a history of kidney disease, intestinal disease, peptic ulcer disease, enteritis, colitis, pancreatitis, hepatitis, who consume excessive alcohol, who plan to become pregnant, or who are over 55 years of age and have a family history of heart disease should consult a doctor and pharmacist before taking iron supplements.
- Individuals with blood disorders who require frequent blood transfusions are also at risk of iron overload and should not take iron supplements without medical supervision.
- Chronic administration of high doses of iron can cause haemosiderosis that clinically resembles haemochromatosis. Iron overload is associated with several genetic diseases, including haemochromatosis. Accumulation of excess iron is being investigated as a potential contributor to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
- In patients undergoing angioplasty caution should be used since an intravenous loading dose of vitamin B6, vitamin B12 and folic acid , followed by oral administration taken daily after coronary stenting, might actually increase restenosis rates. Due to the potential for harm, this combination of vitamins should not be recommended for patients receiving coronary stents and for those who had recently undergone angioplasty.
Drug Interactions:
- Allopurinol may increase iron storage in the liver and should not be used concomitantly with iron supplements.
- Aminosalicylic acid may cause a malabsorption syndrome (weight loss, iron and vitamin depletion, steatorrhoea).
- Long term use of Aspirin and NSAIDs can cause mucosal damage and bleeding throughout the gastrointestinal tract. Chronic blood loss associated with the long-term use of these agents may contribute to iron deficiency anaemia. Since iron supplements may also cause gastrointestinal side effects, patients should not use them concurrently with NSAIDs unless recommended by a physician.
- Chloramphenicol reduces the response to iron therapy in iron-deficiency anaemia.
- Iron supplements and dimercaprol may combine in the body to form a harmful chemical.
- Concomitant administration of iron and Tetracyclines results in decreased effectiveness of iron.
- Concomitant administration of iron and Ciprofloxacins results in decreased effectiveness of the latter.
- Carbamazepine shows drug interactions with niacinamide and vitamin B6
- Amiodarone, Cycloserine, Ethionamide, Fosphenytoin, Hydralazine, Isoniazid, Pencillamine, Phenobarbital, Phenytoin, Theophylline, Valproic acid, Alcoholic beverages are known to have drug interactions with Vitamin-B6
Pregnancy and lactation:
- The use of iron supplements during pregnancy is considered an accepted and safe recommendation which benefits both the mother and the infant. However , because of negative interactions of iron on intestinal absorption of other divalent minerals, supplemental hematinic doses should be as low as possible while fulfilling their purpose.
- Pregnant and lactating mothers should not exceed the U.S RDA i.e., daily amount of vitamins that the FDA has established as sufficient to maintain the nutritional health of persons in various age groups and categories.
- Dosage could exceed U.S RDA limits only when prescribed by Physicians based on the need of the pregnant or lactating woman
References:
The Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Iron Preparations
Instant Pharmacology by Kourosh Saeb-Parsy
New protein food Volume 1 technology part A by Aaron M. Altschul
Manganese and birth outcome
Zinc and copper in pregnancy, correlations to fetal and maternal complications
Benefits of Copper
Disclaimer:
- Information provided above is for reference purpose only and has been compiled for use by healthcare practitioners. Please consult your physician to understand how the product affects you, its dosages, side-effects and further information.
- Remember, keep this and all other medicines out of the reach of children, never share your medicines with others, and use this medication only for the indications prescribed by your physician.
- Every effort has been made to ensure that the information provided by Pharma Synth Formulations Ltd. (‘PSFL’) is accurate, up-to-date, and complete, but no guarantee is made to that effect. PSFL does not endorse drugs, diagnose patients or recommend therapy and is an informational resource designed to assist licensed healthcare practitioners in caring for their patients and/or to serve consumers viewing this service as a supplement to, and not a substitute for, the expertise, skill, knowledge and judgment of healthcare practitioners. PSFL does not assume any responsibility for any aspect of healthcare administered with the aid of information provided. The information contained herein is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, warnings, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or adverse effects. If you have questions about the drugs you are taking, check with your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.